Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a groundbreaking technique that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing them with relevant context from external documents before generating responses. This approach offers several critical advantages:
- Reduces Hallucinations: Grounds answers in actual data instead of relying solely on model training
- Private Data Support: Allows models to work with proprietary or confidential information
- Improved Accuracy: Significantly enhances response relevance and correctness
- Extended Knowledge: Enables answering questions beyond the model’s training data
- Cost Efficiency: Local execution eliminates expensive API calls
Architecture Overview
A complete local RAG pipeline consists of four essential components working in harmony:
🦙 Ollama
Local LLM Runtime enabling large language models to run on your machine without cloud dependencies.
📚 LlamaIndex
Orchestration framework handling document loading, vector indexing, query processing, and response generation.
🗄️ ChromaDB
Vector database storing embeddings and enabling semantic similarity search for relevant document retrieval.
🔢 Embedding Models
Text representation models (like nomic-embed-text) converting documents into numerical vectors.
Pipeline Data Flow
Here’s how data flows through the complete RAG pipeline:
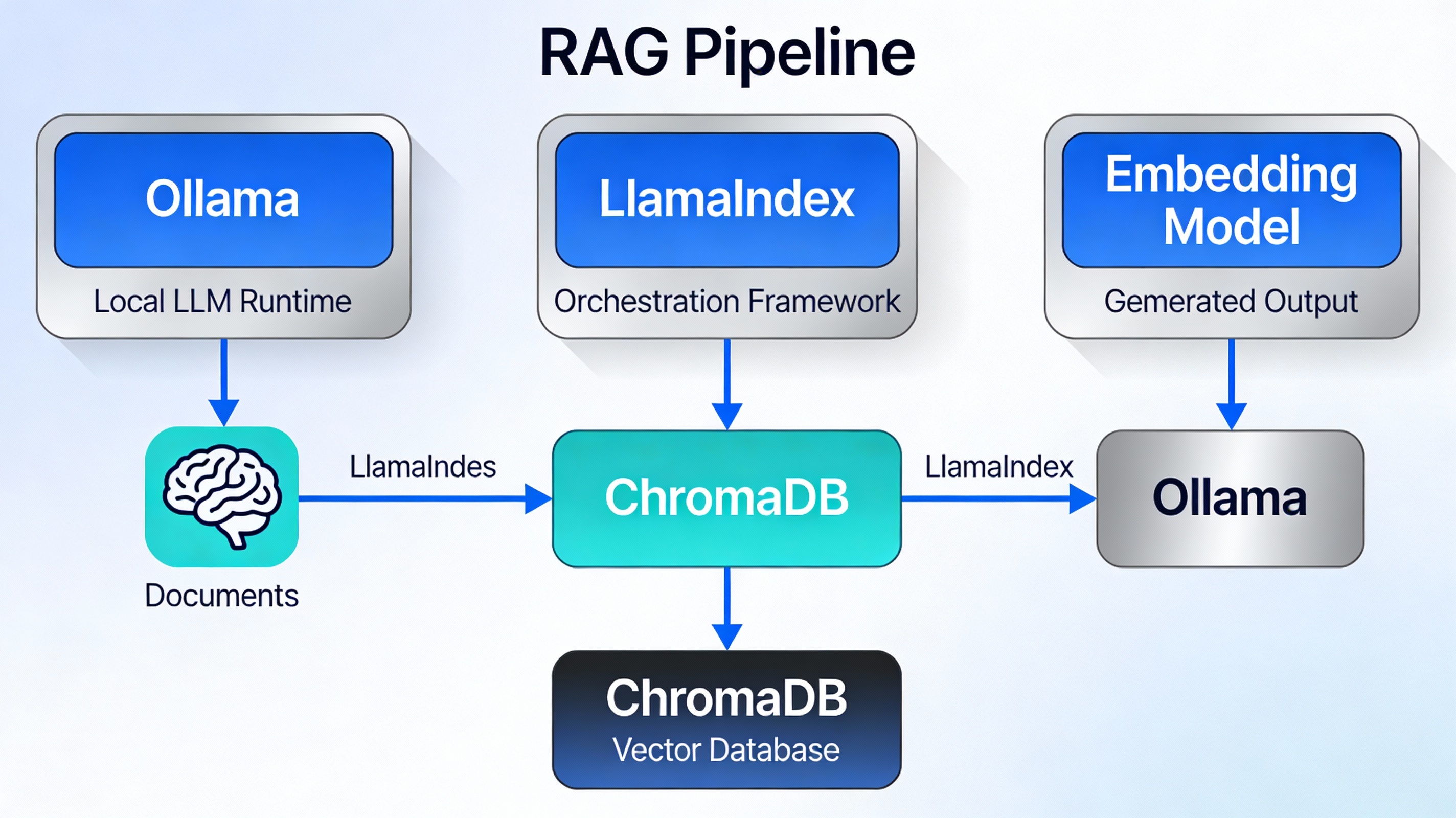
Documents are ingested, converted to embeddings, stored in ChromaDB, and retrieved based on query similarity to provide context to the LLM
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
| Component | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| RAM | 8 GB | 16+ GB |
| Storage | 10 GB free | 25+ GB free |
| GPU | Optional | Recommended (NVIDIA/AMD) |
| Processor | Dual-core | Quad-core or better |
Software Requirements
- Python 3.8 or higher
- pip package manager (usually included with Python)
- Terminal or Command Prompt access
- Internet connection (for downloading models and dependencies)
Installation & Setup
Step 1: Install Ollama
Ollama is the foundation that runs your LLM locally. Choose the installation method for your operating system:
On Linux:
$ sudo systemctl start ollama
On macOS:
Download from ollama.com and follow the installation wizard.
On Windows:
Download the Windows installer from the Ollama website and run the executable.
Step 2: Create a Python Virtual Environment
Isolating your project dependencies prevents conflicts with other Python projects:
Using Conda:
$ conda activate rag-pipeline
Using venv:
$ source rag-pipeline/bin/activate # Linux/Mac
$ rag-pipeline\Scripts\activate # Windows
Step 3: Install Required Python Packages
Install all necessary dependencies with a single pip command:
$ pip install llama-index-embeddings-ollama
$ pip install llama-index-vector-stores-chroma
$ pip install chromadb llama-index llama-index-readers-file
pip install llama-index llama-index-llms-ollama llama-index-embeddings-ollama llama-index-vector-stores-chroma chromadb llama-index-readers-fileStep 4: Download Models
Pull the embedding and language models using Ollama. This step requires internet connectivity:
Recommended Setup:
$ ollama pull llama3.1:8b
Alternative Models:
$ ollama pull neural-chat
$ ollama pull dolphin-mixtral
To verify your models are installed:
Building the RAG Pipeline
Step 1: Import Required Libraries
Start by importing all necessary components from LlamaIndex and related libraries:
import chromadb
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader, Settings
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core import StorageContext
from llama_index.vector_stores.chroma import ChromaVectorStore
from llama_index.embeddings.ollama import OllamaEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.ollama import OllamaStep 2: Configure Embedding and LLM Models
Set up the embedding model for converting documents to vectors and the LLM for generating responses:
# Set embedding model
emb_fn = "nomic-embed-text"
Settings.embed_model = OllamaEmbedding(model_name=emb_fn)
# Set LLM model
Settings.llm = Ollama(model="llama3.1:8b", request_timeout=120.0)Configuration Parameters Explained:
Step 3: Load Your Documents
Load documents from a directory using SimpleDirectoryReader, which automatically handles multiple file formats:
# Create a ./data directory and add your documents
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="./data/").load_data()
# Verify loading
print(f"Loaded {len(documents)} documents")
print(documents[0].get_content()[:200])Step 4: Create Vector Database
Initialize ChromaDB to store embeddings and enable semantic search:
# Initialize ChromaDB with persistent storage
db = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="./chroma_db/")
# Create or retrieve a collection
chroma_collection = db.get_or_create_collection("documents")
# Setup vector store for LlamaIndex
vector_store = ChromaVectorStore(chroma_collection=chroma_collection)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)Step 5: Build Vector Index
Create the vector index from your documents using chunking for optimal retrieval:
# Create vector index with document chunking
vector_index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
storage_context=storage_context,
transformations=[SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=20)]
)Chunking Parameters:
Step 6: Create Query Engine
Build the query engine that will retrieve documents and generate responses:
# Create query engine with refinement mode
query_engine = vector_index.as_query_engine(
response_mode="refine",
similarity_top_k=10
)Response Mode Options:
Complete Code Implementation
Here’s a production-ready implementation you can use as a starting template:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Complete Local RAG Pipeline Implementation
Using LlamaIndex + Ollama + ChromaDB
"""
import chromadb
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader, Settings, PromptTemplate
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core import StorageContext
from llama_index.vector_stores.chroma import ChromaVectorStore
from llama_index.embeddings.ollama import OllamaEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.ollama import Ollama
# ===== Configuration =====
EMBEDDING_MODEL = "nomic-embed-text"
LLM_MODEL = "llama3.1:8b"
DATA_DIR = "./data/"
DB_PATH = "./chroma_db/"
CHUNK_SIZE = 512
CHUNK_OVERLAP = 20
# ===== Setup Phase =====
def setup_models():
"""Configure embedding and LLM models"""
print("Configuring models...")
Settings.embed_model = OllamaEmbedding(model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL)
Settings.llm = Ollama(model=LLM_MODEL, request_timeout=120.0)
print("✓ Models configured successfully")
def load_documents():
"""Load documents from directory"""
print(f"Loading documents from {DATA_DIR}...")
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir=DATA_DIR).load_data()
print(f"✓ Loaded {len(documents)} documents")
return documents
def setup_vector_db(documents):
"""Create and populate vector database"""
print("Setting up vector database...")
# Initialize ChromaDB
db = chromadb.PersistentClient(path=DB_PATH)
chroma_collection = db.get_or_create_collection("documents")
# Create storage context
vector_store = ChromaVectorStore(chroma_collection=chroma_collection)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
# Build index
print("Building vector index (this may take a moment)...")
vector_index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
storage_context=storage_context,
transformations=[SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=CHUNK_SIZE, chunk_overlap=CHUNK_OVERLAP)]
)
print("✓ Vector database setup complete")
return vector_index
def create_query_engine(vector_index):
"""Create configured query engine"""
query_engine = vector_index.as_query_engine(
response_mode="refine",
similarity_top_k=10
)
# Customize prompts (optional)
qa_template = PromptTemplate(
"You are an expert assistant answering questions based on provided context.\n"
"Context:\n{context_str}\n"
"Question: {query_str}\n"
"Provide accurate, helpful answers based only on the provided context.\n"
"Answer: "
)
query_engine.update_prompts({
"response_synthesizer:text_qa_template": qa_template
})
return query_engine
# ===== Query Function =====
def ask(query_engine, question: str):
"""Query the RAG pipeline"""
response = query_engine.query(question)
return response
# ===== Main =====
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize pipeline
setup_models()
documents = load_documents()
vector_index = setup_vector_db(documents)
query_engine = create_query_engine(vector_index)
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("RAG Pipeline Ready!")
print("="*50 + "\n")
# Example queries
questions = [
"What are the main topics covered?",
"Can you summarize the key concepts?",
"What are the best practices mentioned?"
]
for q in questions:
print(f"Q: {q}")
response = ask(query_engine, q)
print(f"A: {response}\n")Querying Your Data
Basic Query
The simplest way to query your RAG pipeline:
response = query_engine.query("What is the main concept?")
print(response)Query with Source Information
Retrieve response along with source documents for verification:
response = query_engine.query("Explain the core principles")
print(f"Answer: {response}")
print("\nSource Documents:")
for node in response.source_nodes:
print(f"- {node.get_content()[:150]}...")
print(f" Score: {node.score:.2f}\n")Batch Processing Multiple Questions
questions = [
"What are the key features?",
"How does it work?",
"What are the benefits?",
"What are the limitations?"
]
results = {}
for q in questions:
response = query_engine.query(q)
results[q] = str(response)
print(f"Q: {q}\nA: {response}\n")Advanced Query Options
# Use different response modes
query_engine_compact = vector_index.as_query_engine(response_mode="compact")
response_compact = query_engine_compact.query("Your question")
# Adjust similarity threshold
query_engine_strict = vector_index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5)
response_strict = query_engine_strict.query("Your question")
# Custom parameters
query_engine_custom = vector_index.as_query_engine(
response_mode="refine",
similarity_top_k=15,
verbose=True
)Best Practices
1. Document Preparation
- Clean Data: Remove headers, footers, and irrelevant content before loading
- Consistent Format: Standardize document structure for better indexing
- Remove Duplicates: Avoid indexing the same content multiple times
- Proper Encoding: Ensure UTF-8 encoding for all text files
2. Optimize Chunking Strategy
| Chunk Size | Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| 256 | Small documents, Q&A | Fast, granular retrieval | Lost context |
| 512 | Balanced (default) | Good balance, fast | May be insufficient |
| 1024 | Long documents | More context preserved | Slower, more expensive |
3. Model Selection Strategies
⚡ For Speed
Use 3B-7B parameter models like Mistral 7B or Neural Chat for faster responses
🎯 For Accuracy
Use 13B-70B models for better quality responses (slower)
⚖️ Balanced
Llama3.1:8b provides great speed/quality tradeoff
4. Memory Management
Avoid rebuilding indices by saving and loading them:
from llama_index.core import load_index_from_storage
# First run - build index
vector_index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents, storage_context=storage_context)
# Subsequent runs - load from storage
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="./storage")
vector_index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context)
query_engine = vector_index.as_query_engine()5. Performance Tuning
- Reduce similarity_top_k: Lower values (5-10) are faster but may miss relevant context
- Cache Queries: Store results of frequent questions to avoid reprocessing
- Monitor Timing: Log query times to identify bottlenecks
- Use GPU: Configure Ollama to use GPU for 5-10x speedup
Troubleshooting
Issue: “Connection refused” error with Ollama
Solution: Ensure Ollama service is running:
Or check if it’s already running as a background service.
Issue: Out of Memory (OOM) Error
Solutions:
- Reduce chunk_size from 512 to 256
- Use smaller models (3B instead of 13B)
- Reduce similarity_top_k from 10 to 5
- Increase system RAM or use swap space
Issue: Very Slow Response Times
Solutions:
- Increase request_timeout in Ollama configuration
- Use a smaller, faster model
- Reduce similarity_top_k parameter
- Enable GPU acceleration for Ollama
- Reduce the number of documents indexed
Issue: Poor Quality Responses
Solutions:
- Use a larger, more capable model
- Improve document preparation and formatting
- Adjust chunk_size to better split semantic units
- Customize the system prompt in PromptTemplate
- Increase similarity_top_k to provide more context
Issue: Model Not Found in Ollama
Solution: Pull the model first:
$ ollama list # Verify it appears here
- ✅ Complete Privacy: All data and processing stays on your machine
- ✅ Zero API Costs: No expensive cloud service subscriptions
- ✅ Full Control: Customize models and parameters for your needs
- ✅ Offline Capability: Works without internet after initial setup
- ✅ Scalability: Can be deployed to production environments
Next Steps
- Prepare your documents and organize them in a ./data directory
- Experiment with different chunk sizes and response modes
- Test various embedding and LLM models to find your optimal balance
- Consider building a web interface (FastAPI, Streamlit, Flask)
- Monitor performance and optimize based on real-world usage patterns
- Implement caching for frequently asked questions
- Deploy to production if handling multiple concurrent users
Further Learning Resources
- LlamaIndex Documentation: https://docs.llamaindex.ai/
- Ollama Model Library: https://ollama.com/library
- ChromaDB Documentation: https://docs.trychroma.com/
- LLama Models: https://huggingface.co/meta-llama
- Embedding Models: https://huggingface.co/models?sort=downloads&search=embedding
